May, 9, 2024

By Dr Kiruthika Natarajan, Dr Manoj Thibbotuwawa, and Dr Suresh Babu
While Sri Lanka is recovering from its worst economic crisis since independence, significant concerns remain as 42% of the households still adopt food coping strategies which severely affect both quantity and the quality of protein consumption. Pulses are rich in quality and quantity of proteins, however, pulses comprise only 8% of Sri Lanka’s per capita protein supply. Also, the per capita availability of pulses for consumption in Sri Lanka through local production and imports is just over half the recommended quantity for a balanced diet. Against this backdrop, this blog analyses the trends in pulse production, consumption requirements, trade, and associated policy options to provide recommendations for sustainable pulse production to meet the dietary consumption and nutritional requirements of Sri Lanka’s growing population.
Over the years, the cultivation of pulses in Sri Lanka has undergone notable shifts. The area under pulses cultivation increased by 7.87% from 1974–1990 but decreased by 1.56% during 1991–2022. Similarly, overall pulse production increased by 8.31% between 1974–1990 but exhibited a meagre growth rate (0.09%) from 1991–2022 (Table 1). Pulses currently occupy less than 1% of agricultural land. The daily Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of pulses for an average sedentary man is 40 g (15 kg/year/person. But current domestic production of pulses contributes 1.7 kg/year/person, which is a mere 11% of the requirement.
Table 1: Growth in area and production of major pulses in Sri Lanka

Source: Socio Economics and Planning Centre (SEPC)
Pulse trade is an important strategy to meet the Sri Lankans' dietary requirements. During the 1960s, Sri Lanka imported up to 50,000–60,000 mt of dry beans, chickpeas, and dry lentils. But between 1974 and 1990 these imports were negligible until they started to rise in the 1990s (Figure 1). This increase can be attributed partly to the introduction of alternative pulses, such as lentils, and the low prices of these alternative sources in international markets. However, the total pulses imports contribute 6.8 kg/year/person, which is about 46% of the requirement.

Source: Food and Agriculture Organization
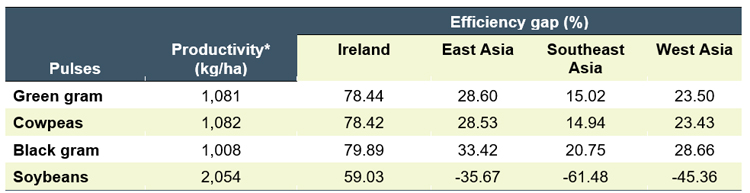
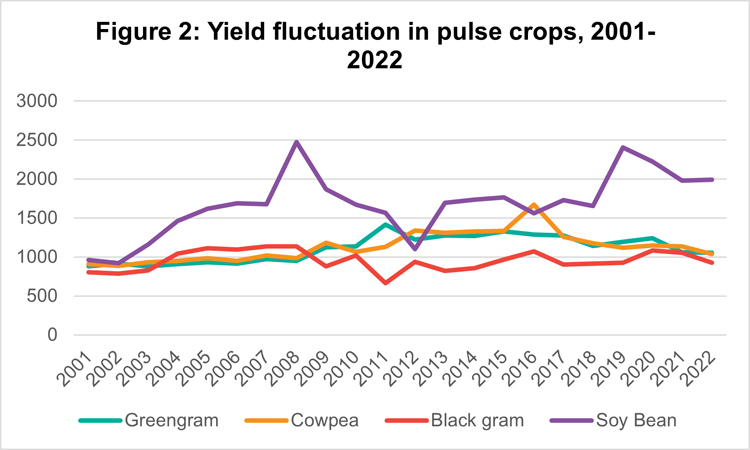
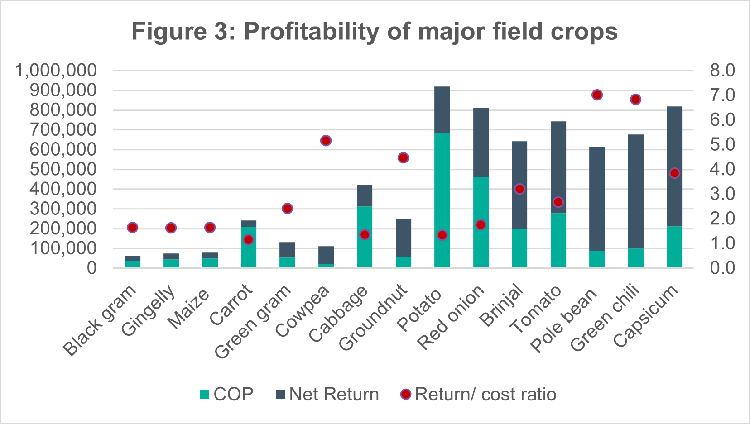
The local supply of pulses through domestic production and imports amounts to 8.5 kg/year/person (58% of the requirement). Filling this gap merely by increasing the production of pulses locally is challenging due to the existing productivity and efficiency gap. All Sri Lankan pulses have a huge efficiency gap (EG) relative to the leading producing regions globally (Table 2). Bridging this gap is challenging since pulse productivity declined for the past six years after remaining stagnant since the 2010s (Figure 2). Moreover, this has led to low returns on investments for most of the pulses (Figure 3).
Table 2: Productivity and efficiency gap of pulse production in Sri Lanka
Source: Socio Economics and Planning Centre (SEPC)
Source: Socio Economics and Planning Centre (SEPC)
Source: Socio Economics and Planning Centre (SEPC)
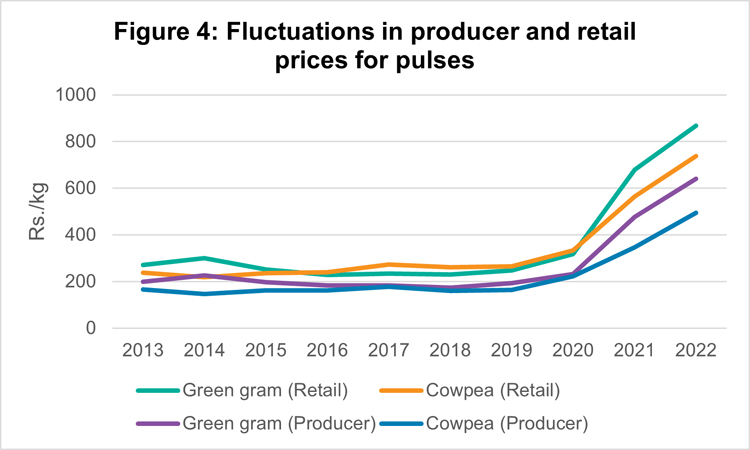
Price stagnation is a common phenomenon in pulse trade (Figure 4). Since 2019, both the producer and retail prices have trended upward due to the external pressures from the COVID-19 pandemic and Sri Lanka’s deteriorating macroeconomic situation. However, poor marketing facilities and unstable prices coupled with a widening retailer-producer price gap have placed pulse producers in a precarious position. On the other hand, the farmgate price of pulses is lower than the import price after the imposition of the tariff, indicating a very protectionist system (Table 3). Such protectionist policies to safeguard local farmers may not be conducive to the long-term growth of the sector and to ensuring food and nutrition security in the country.
Source: DOA (2022). AgStat, Department of Agriculture of Sri Lanka.
Table 3: Import tariffs and prices of pulses (Rs/kg)

Source: Import Tariff – Sri Lanka Customs; Socio Economics and Planning Centre (SEPC)
Given the current level of pulse production in Sri Lanka, reviving the pulse sector will require both short- and long-term strategies to address the various challenges including poor agricultural practices, inappropriate government policies, market dynamics, and climate change. The short-term goal should be to improve production and productivity gradually while filling gaps in supply to achieve dietary requirements through imports. The import basket should include pulses like red lentils that do not compete directly with local pulses to meet the population’s protein requirements, especially the poor. Imports can also help fill the supply gap and stabilize prices.
Long-term strategies in increasing the role of pulses in generating rural income and providing food security must focus on coordinated efforts involving policy support, research and extension, and market and demand considerations. All these efforts should especially focus on areas with huge untapped potential like diversifying the sector with underutilised pulse crops like Kollu, Pigeon peas and Chickpeas in dry upland cropping systems and increasing pulses’ area with improved input use efficiency under the “pulse in rice fallow” method. Successfully marketing pulse crops in Sri Lanka depends on crop quality, market demand, pricing, and effective distribution channels which can be achieved by improved collaboration among value chain stakeholders, promoting value addition, market intelligence through digital technologies, improved storage and transport facilities and consumer education and awareness on pulses’ benefits and how to incorporate them into meals.
Video Story