October, 11, 2023

Complied by the Securities and Exchange Commission of Sri Lanka
Subsequent to the enactment of the new Securities and Exchange Commission of Sri Lanka (SEC) Act No. 19 of 2021 and the provisions enabled thereto, the SEC is presently working with the Colombo Stock Exchange (CSE) to introduce Regulated Short Selling through a Securities Borrowing and Lending mechanism.
In August 2021, under the guidance of the SEC, a Delivery vs. Payment (DvP) settlement mechanism was successfully implemented at the CSE. As the next step, the wheels are already set in motion to implement a fully fledged Central Counterparty (CCP) mechanism, and the SEC and CSE teams are preparing the necessary regulations and making the requisite infrastructure modifications with a view to introducing the same to the Sri Lankan market. A CCP will offer significant benefits to the financial market in Sri Lanka by enhancing post-trade risk management and unlocking the potential to launch new capital market products.
In the above backdrop, the introduction of Regulated Short Selling through Securities Borrowing and Lending provides an impetus for economic growth at this hour of need. Capital markets act as powerful engines that contribute towards the growth of an economy, and the enhanced liquidity attributed by the introduction of Regulated Short Selling through Securities Borrowing and Lending would aid in developing the local capital market and the economy at large.
The Basic Concept of Securities Borrowing and Lending
Securities Borrowing and Lending (SBL) is a mechanism where an investor can lend securities to an identified borrower for a pre-determined period at an agreed upon fee.
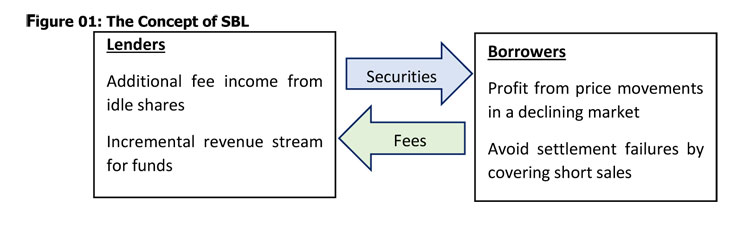
Key Benefits of SBL
From a Lender’s perspective, SBL provides a mechanism to utilize an idle portion of the Lender’s portfolio to gain additional income, this would especially be beneficial for long term investors such as pension funds, Collective Investment Schemes and insurance companies. From the Borrower’s perspective it provides the opportunity to make profits during a market downturn via Short Selling. Thus improving market liquidity, efficiency and price discovery.
Short Selling which is discussed next in this article, is a mechanism that lets an investor profit from falling stock prices. Having a SBL mechanism in place ensures timely securities settlement and safeguards against the risk of a security default.
During turbulent times, there could be situations where the demand for a security could spike up suddenly, and the participants who are short would be forced to close out their position at a significant loss, causing a further spike in the prices. These spikes could subside once demand abates, but they create unnecessary volatility in the market. Such situations are called ’short squeezes’. Short squeezes can be attenuated to some extent by the presence of an active SBL market as short sellers can hold on to their position longer by borrowing securities.
Several types of participants can use SBL to support their cash market activities. Thus, a fully functional SBL mechanism implies more participation in the cash market.

Regulated Short Selling
What is a short Selling?
Short Selling is a financial practice where an investor borrows securities, sells them, and then hope to buy them back at a lower price to make a profit. This practice is often seen as risky and in some cases, even unethical. However, when done within a regulated framework, Short Selling would actually benefit the market by providing liquidity, improving price discovery, and reducing market volatility.
Types of Short Selling
The seller sells securities they do not own, without having set aside any securities to settle the transaction. Since they did not borrow the securities that have been sold, the short seller does not have to pay any borrowing fees. Naked short selling carries settlement risk which has led to many jurisdictions imposing a ban on naked short selling.
A covered short sale is where the seller has arranged to borrow securities prior to executing the Short Selling transaction.

Sale of borrowed securities: As the first step, the seller anticipating falling prices borrows a certain security from a potential Lender at an agreed upon fee and sells it on to a market participant at the market price.
Returning the securities borrowed: As the second step, the seller has to return the borrowed securities to the Lender at the time they are due or when the Lender recalls them. To do so, the Borrower buys the relevant number of securities at the market price subsequently and returns them to the Lender.
Key Benefits of Regulated Short Selling
Market participants expecting the price of an asset to fall as a consequence, contribute important information to the market. Short Sellers are likely to be among the first to realize and signal that an asset is overvalued or even in bubble mode. As a result, short sellers are important contributors to the process of price discovery in the market.
Short sellers contribute to the liquidity of markets by facilitating transactions that otherwise may not materialize irrespective of whether they own the securities they sell through active SBL agreements.
Exposure to both short (selling) and long (buying) positions can help to reduce overall portfolio volatility while also allowing for the addition of considerable risk-adjusted returns.
Potential Risks Associated with Regulated Short Selling and the SBL Mechanism
If the Borrower of the SBL becomes insolvent, the collateral’s value may come down, which would create a loss to the Lender.
If the security value rises after the short sale, short sellers would suffer losses.
Short squeezes where Short Sellers cover in large numbers in response to sudden and strong upward price fluctuations can drive prices against the Short Sellers.
If the Lenders and Borrowers misuse the terms of the agreement for their benefit, it would make the mechanism less attractive.

The International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) principles applicable for short selling are as follows:
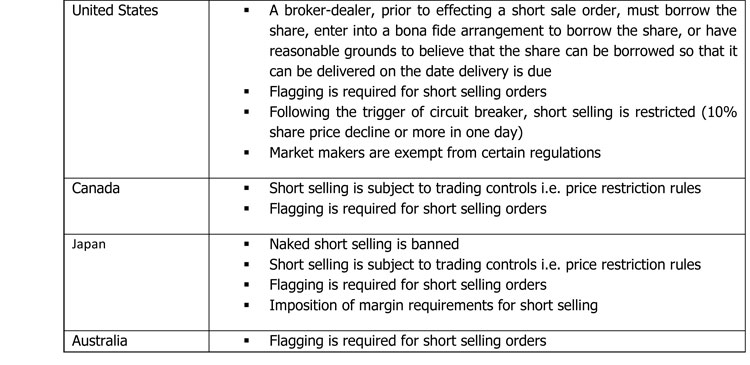
Principle 1: Short Selling should be subject to appropriate controls to reduce or minimize the potential risks that could affect the orderly and efficient functioning and stability of financial markets.
Principle 2: Short Selling should be subject to a reporting regime that provides timely information to the market or to market authorities.
Principle 3: Short Selling should be subject to an effective compliance and enforcement system.
Principle 4: Short Selling regulation should allow appropriate exceptions for certain types of transactions for efficient market functioning and development.
The above principles should be considered by the capital market regulatory authorities in order to effectively regulate Short Selling.
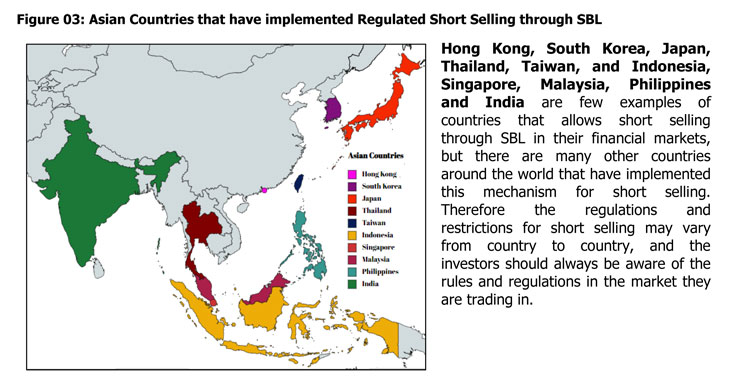
Introduction of Regulated Short Selling through SBL to the Sri Lankan Market
The introduction of Short Selling would act as an enabler to enhance liquidity in the market. The proposed Regulated Short Selling model is to be introduced through a SBL mechanism to address the settlement risk associated with naked Short Selling.
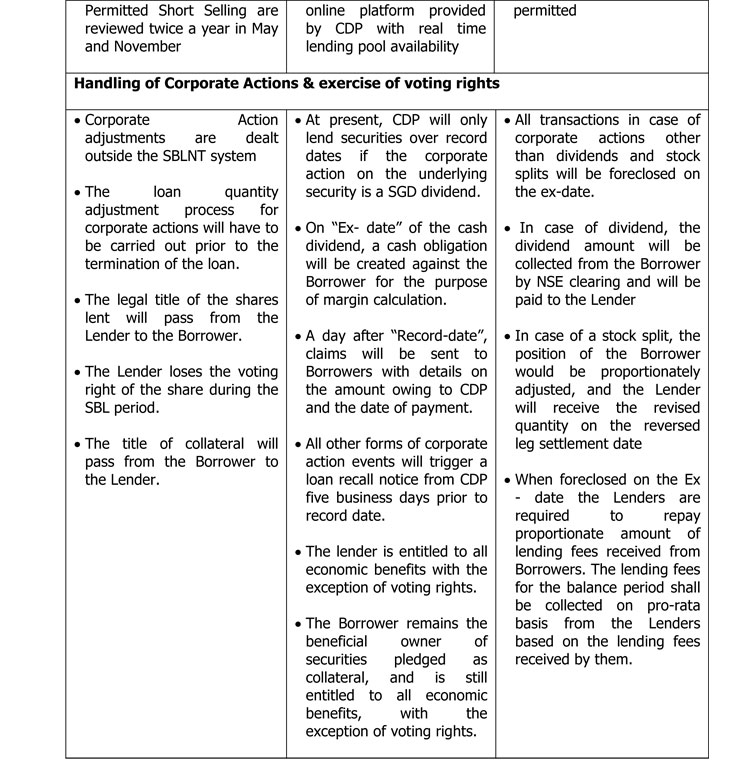
The SEC and CSE has finalized the policy framework for introducing Regulated Short Selling through SBL with the technical expertise received from the Consultant procured under the Financial Sector Modernization Project of the World Bank to support this initiative. The final policy framework and the draft rules developed by the CSE enabling the proposed policy Framework have been approved by the SEC Commission. The proposed framework includes safeguards such as identifying eligible securities for SBL and Short Selling, eligible participants, up-tick rule, maximum quantity of an issued security that can be borrowed under SBL, default handling mechanism and other features such as the process for handling corporate actions etc.
At a juncture where Sri Lanka is seeking to transition from a frontier market to an emerging market, Regulated Short Selling would greatly enhance the depth and breadth of the Capital Market Landscape and lead to enhanced market activity and market growth.
Video Story